 UMAN
UMAN XPLOITATION
XPLOITATION  F
F IVERSE
IVERSE  NVIRONMENTS
NVIRONMENTS UMAN
UMAN XPLOITATION
XPLOITATION  F
F IVERSE
IVERSE  NVIRONMENTS
NVIRONMENTS 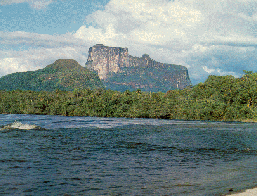 |
"The T.F. Amazonas comprises a variety of
ecological systems which in turn contain many kinds of
habitat and ecological niches: jungle, tropical forrest,
savannah.
|
"The autochthonous populations of the Amazonia have developed after a long process of experimentation that dates millenniums, an assembly of adaptive cultural answers facing the multiple challenges of the ecosystem. These answers have permitted the creation and the maintenance of complex cultural and social systems which are viable and a degree of welfare that is not susceptible to be evaluated according to measures developed by the industrial society to measure quality of life, and that have no negative effects for the ecosystems". (MARNR. V. 1. 1983:193-201)
"Among the cultural patterns implemented by these cultures, who have shown to be adaptive, it is the agricultural system known as agriculture of felling, itinerant and migratory, complemented by hunting, fishing and recolection; the establishment of small and disperse settlements, in agreement with the availability and location of the resources and the adoption of an ideology that gives the indian man a perception of himself as a link in the biotic amazonic system. It is this cultural combination that has permitted them to interact harmonically in the environment".
"The amazonic agricultural system known as migrational agriculture, intenerant or of felling, reproduces in the plot cultivated the same one ecosistema generalized that is found in natural form in the forest. The 'Conuco', little extensive, in the forest surrounded by primary vegetation , is a multi harvest that possesses an estratification that recreates in miniature that of the adjacent primary forest".
"The practic which conforms this agricultural system of conuco, can be summarized in this way:
A. The size of the plot should be reduced and surrounded by forests, in order that its temperature can be maintained relatively low and the biochemical process of bacteria proliferation be retarded and the disappearance of the fungus. The maintenance of a relatively low temperature, helped by the presence of trees inside the cultivated plot , should produce shade and retard the erosion.
B. The falling and burning of trees is a transfer process of the rich nourishments stored in the vegetales to the soil.
C. The regeneration produced in the cultivated plot through the process of secondary succesion is helped by the practice of not cleaning the field.
D. In the cultivated plot the same type of "architecture" of the original forest is reproduced: abundance of shade in the presence of the trunks of the fallen trees that with their roots, retard the erosion and the acumulation in the soil of the decomposing material.
E. The presence of a strange variety of plants, cultivated with different cycles of growth and different requirements of nourishments of the soil" .(VARESE 1977:48-49)
"This agricultural system is complemented with hunting, fishing and recollection.
"For the hunts and the recollection the indians take into account the dispersion of the resources and the periodicity of production in the tropical trees... The hunters know the alimentary habits of their prey and their migratory patterns and they adjust the location of their settlements to these variables".
"As for the fishing, its practice is very productive in the banks of the large rivers which permits greater concentrations of population and greater sedentarism. In the interfluvial ecotypeor of Terra Firm, although the fishing, as productive activity, does not give the same performances, the indians have very efficient and varied technologies, without the fishing becoming a destructive activity" .(CLARK 1982 in MARNR V.1.1983:202-203).
Human presence in the Territory, for thousands of years until the present, is exhibited through four moments: prehispanic, conquest, colony and republic. Over these aspects the singularities of the Territory are specified where, for example to speak of the contact, we have to refer to the year 1744, date in which the first explorations to the interior of the Territory are initiated.
Since 1744 the presence of the diverse catholic congregations (Jesuits, Capuchinos, Franciscans of Pí ritu) exercised their religious activity with periods in which, by diverse reasons, they had to stay away from the Territory. It is since 1933 that a permanent participation exists; in that year the Salesianos arrived to the T. F. A.




©Todos los derechos reservados, se prohibe la
reproducción salvo permiso por escrito del autor.
©All rigths reserved, material duplication is prohibited
without written authorization by its author.